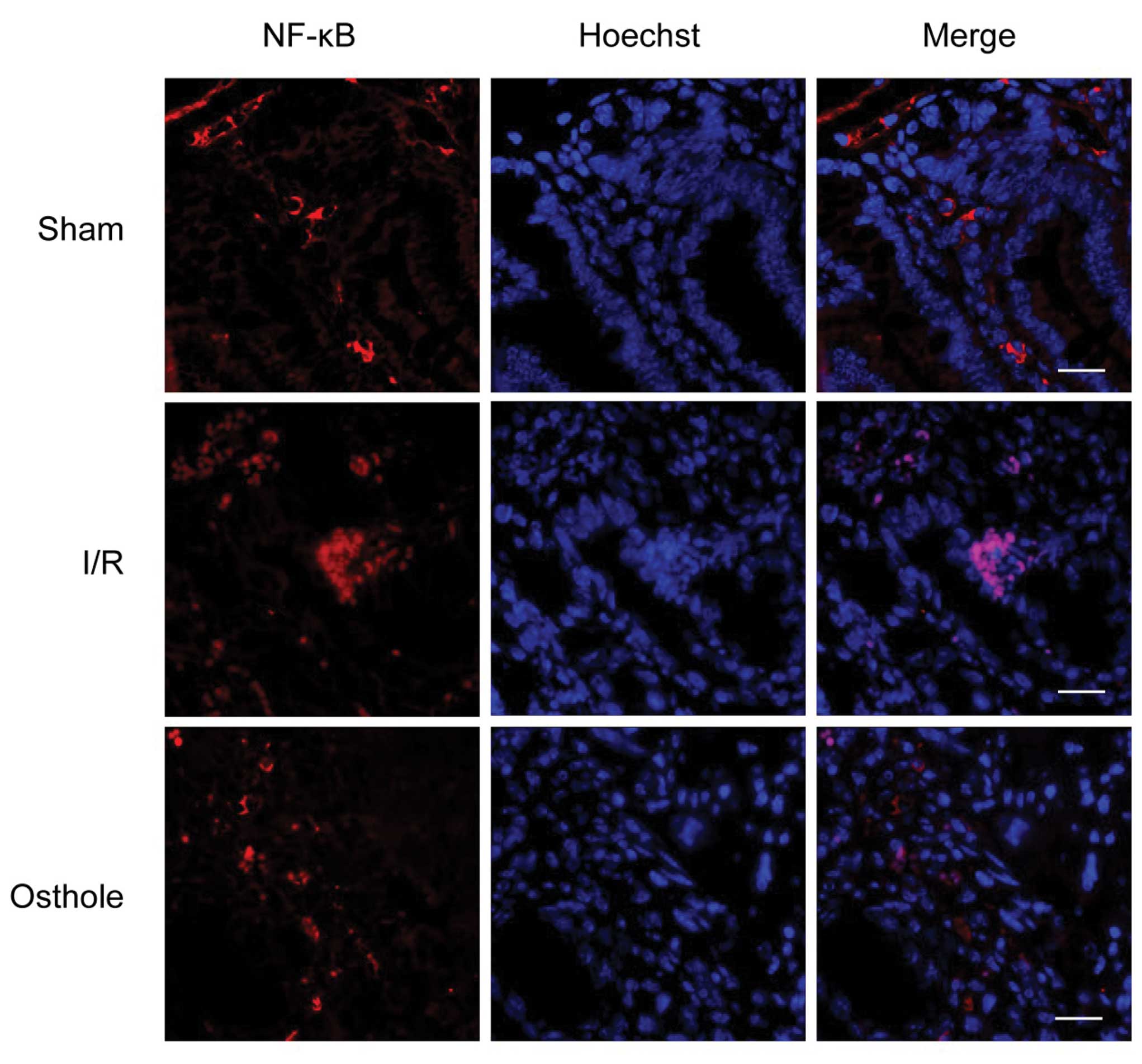
Biotin Supplementation Ameliorates Murine Colitis by Preventing NF-κB Activation - Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology

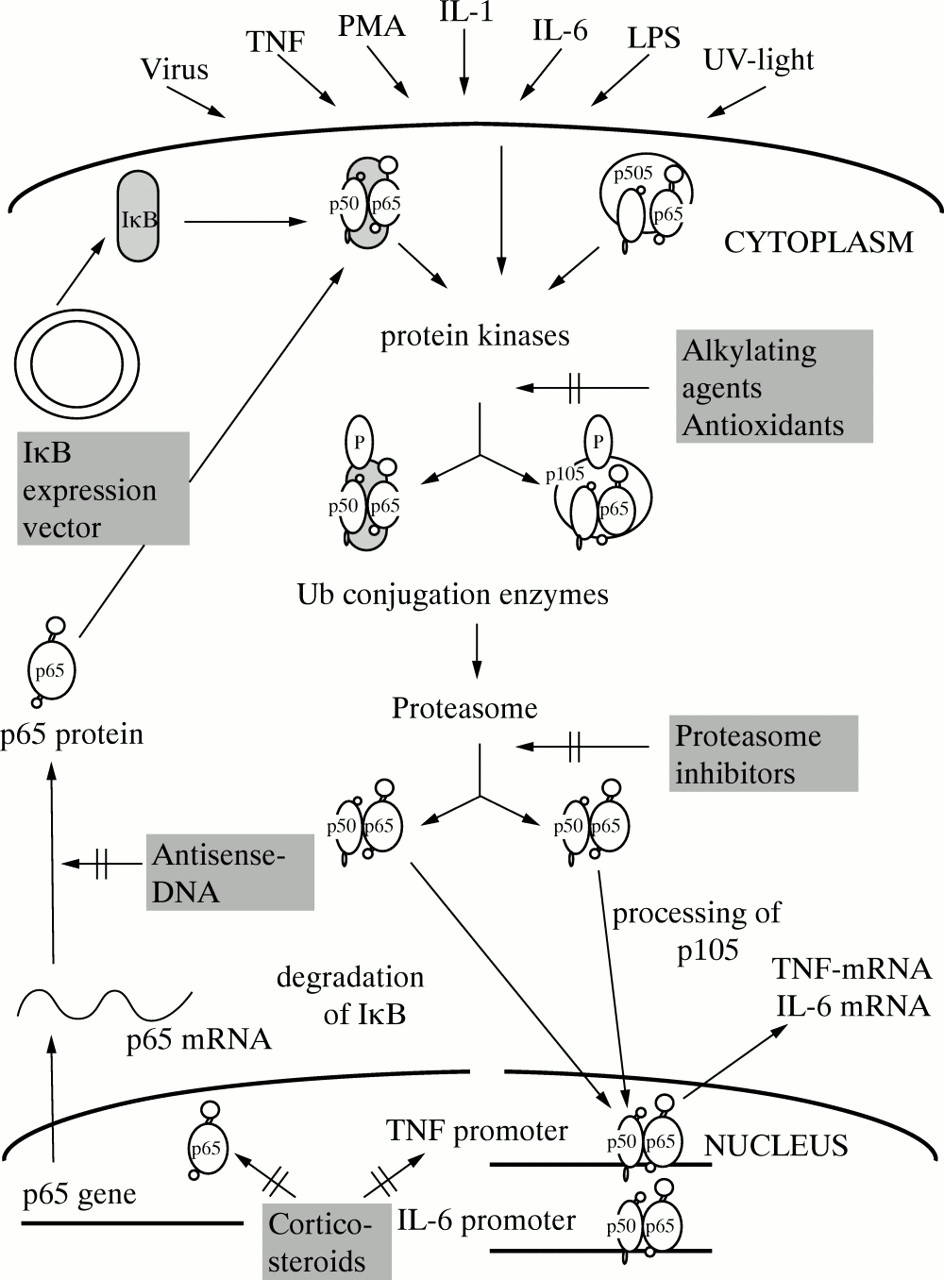
Inhibition of Oxidant-Induced Nuclear Factor-κB Activation and Inhibitory-κBα Degradation and Instability of F-Actin Cytoskeletal Dynamics and Barrier Function by Epidermal Growth Factor: Key Role of Phospholipase-γ Isoform | Journal of Pharmacology and
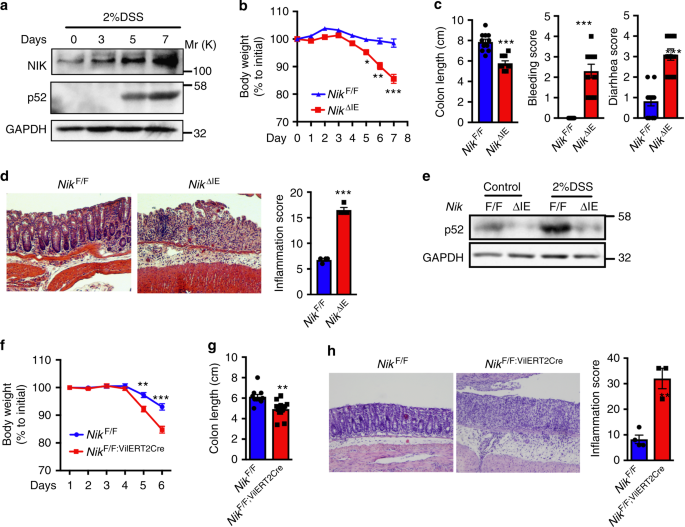
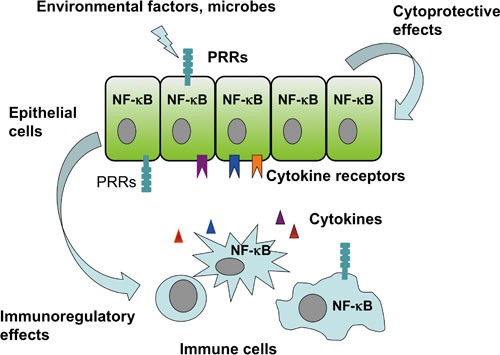
Intestinal non-canonical NFκB signaling shapes the local and systemic immune response | Nature Communications

IKK/NF‐κB and STAT3 pathways: central signalling hubs in inflammation‐mediated tumour promotion and metastasis | EMBO reports

NF-κB Is a Central Regulator of the Intestinal Epithelial Cell Innate Immune Response Induced by Infection with Enteroinvasive Bacteria | The Journal of Immunology
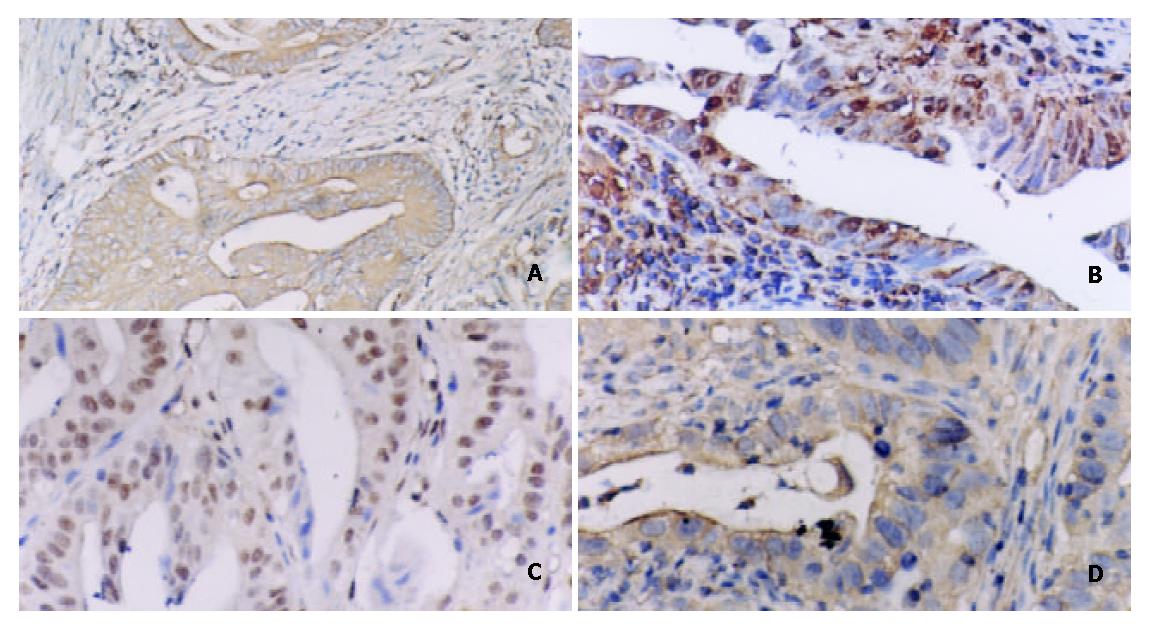
Expression of nuclear factor-kappa B and target genes in gastric precancerous lesions and adenocarcinoma: Association with Helicobactor pylori cagA (+) infection
PLOS ONE: Role of TLR4/NF-κB in Damage to Intestinal Mucosa Barrier Function and Bacterial Translocation in Rats Exposed to Hypoxia

pIC-and TNF-induced IEC apoptosis is independent of NF-κB signaling,... | Download Scientific Diagram

NEMO Prevents RIP Kinase 1-Mediated Epithelial Cell Death and Chronic Intestinal Inflammation by NF-κB-Dependent and -Independent Functions: Immunity

Persistent Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibition Downregulates NF-κB, Resulting in Chronic Intestinal Inflammation in the Min/+ Mouse Model of Colon Tumorigenesis | Cancer Research

Suppression of NF-κB Activation by Entamoeba histolytica in Intestinal Epithelial Cells Is Mediated by Heat Shock Protein 27* - Journal of Biological Chemistry

Intestinal non-canonical NFκB signaling shapes the local and systemic immune response | Nature Communications

ROS Production and NF-κB Activation Triggered by RAC1 Facilitate WNT-Driven Intestinal Stem Cell Proliferation and Colorectal Cancer Initiation: Cell Stem Cell

LGR5 constitutively activates NF‐κB signaling to regulate the growth of intestinal crypts - Lai - 2020 - The FASEB Journal - Wiley Online Library

Nuclear factor κB is activated in macrophages and epithelial cells of inflamed intestinal mucosa - Gastroenterology

Figure 2. | Persistent Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibition Downregulates NF-κB, Resulting in Chronic Intestinal Inflammation in the Min/+ Mouse Model of Colon Tumorigenesis | Cancer Research